This article provides a comprehensive comparison of healthcare in Germany and India, focusing on key aspects such as coverage, financing, appointment logistics, challenges, and service provisions. By exploring these differences, Indian expats can better navigate their healthcare options and ensure they receive the care they need in their new environment.
Table of Contents
As Indian expats settle into their new lives in Germany, understanding the nuances of the healthcare systems in both countries becomes essential. The healthcare landscape varies significantly between Germany and India, shaped by different cultural, economic, and structural factors.
Financing and Coverage
Let us now delve deeper into the subject of costs. The financing and coverage of healthcare costs in Germany and India differ significantly, reflecting their contrasting healthcare systems and economic structures.
Germany: Comprehensive Coverage with Minimal Out-of-Pocket Costs
- Financing: Germany’s healthcare system is primarily financed through statutory health insurance contributions, which are shared between employers and employees. The contribution rate is 14.6 % of gross wages, with an additional average supplementary contribution of 1 %. This system ensures a stable funding source for comprehensive healthcare coverage.
- Coverage: The German system provides extensive coverage for most medical costs, including:
- Hospital care
- Outpatient services
- Prescription drugs (with minimal co-payments)
- Preventive care
- Mental health services

This comprehensive coverage results in minimal out-of-pocket costs for patients. The system is designed to protect individuals from financial hardship due to medical expenses.
- Payment Process: In Germany, patients rarely make direct cash payments to doctors. Instead, the health insurance funds handle payments to healthcare providers. Patients may receive invoices by post for non-mandatory services, such as travel vaccines.
India: Variable Coverage with Significant Out-of-Pocket Expenses
- Financing: India’s healthcare system is characterized by a mix of public and private financing, with a significant portion of healthcare costs borne directly by patients. The government’s expenditure on healthcare is relatively low compared to many developed countries.
- Coverage: Healthcare coverage in India is fragmented and varies widely. Public healthcare services are available, but often underfunded and overburdened. Private insurance plans are available but not universally adopted
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: A significant portion of healthcare costs in India are paid out-of-pocket by patients. This includes expenses for:
- Hospital treatments
- Outpatient services
- Medications
- Diagnostic tests
The high out-of-pocket expenses can lead to financial hardship for many families, especially for major medical procedures or chronic conditions.
| Public Insurance | Private Insurance | |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility Criteria | Everyone who are legal or long term resident in Germany | High income earners, freelancers, self-employed workers |
| Cost | 14.6% of gross salary (50% paid by employee, 50% by employer) | Varies based on factors like age, health condition, and coverage |
| Coverage | inpatient and outpatient treatment, medication, dental care, medical aids, pregnancy and childbirth | Includes all services offered in public insurance, some additional services like private room in a hospital, private medical bills, etc. |
| Coverage for families | Immediate dependent families are included free of charge | Family members are included for an extra fee |
| Medical Bills | Medical bills are covered by insurance, no need to pay upfront | Pay medical bills upfront and insurance reimburses it |
Key Comparisons
- Accessibility: India offers more direct access to specialists, while Germany’s referral system aims to manage resources more efficiently.
- Wait Times: Germany may have longer wait times for specialist appointments, while India’s system can lead to unpredictable waiting times at clinics.
- Quality Consistency: Germany provides more consistent quality across regions, whereas India shows significant variations between urban and rural areas.
- Emergency Response: Germany’s standardized emergency system contrasts with India’s more varied approach to emergency care.
- Appointment Flexibility: Indian clinics often offer more flexible hours and walk-in services, while German clinics typically adhere to more structured schedules.
Hence, while Germany’s system is more structured and offers consistent quality, India’s system provides more direct access and flexibility. However, the quality and accessibility in India can vary greatly depending on location and economic factors.
Navigating Medical Appointments
Germany: Structured and Referral-Based Access
- Referral System: In Germany, the referral system (Überweisung) from a General Practitioner (Hausarzt) to specialists is still in place, but it has become more flexible. While referrals are recommended and can expedite the process, patients can now directly access many specialists without a referral. However, using the referral system often results in shorter waiting times and better coordination of care.
- Appointment Scheduling: Patients in Germany should plan for potential waiting times when scheduling appointments, especially with specialists. Wait times can vary from a few days to several weeks, depending on the speciality and urgency of the case.
- Quality of Care: Germany offers universal quality of care across urban and rural areas, with well-equipped hospitals and clinics throughout the country. This consistency in quality is a significant advantage of the German healthcare system.
- Health Insurance Card: Patients must carry their health insurance card (Gesundheitskarte) to all medical appointments. This electronic card contains essential information and is crucial for accessing healthcare services.
- Emergency Services: Emergency medical services in Germany are accessible by walking into emergency centres (Notaufnahme) or calling the emergency number 112. This system ensures quick response to medical emergencies.
- Clinic Hours: German medical practices typically operate during standard business hours, with many closing in the afternoon on certain days (often Wednesdays and Fridays). Some clinics offer extended hours or weekend services to accommodate working patients.
India: Direct Access and Variable Quality
- Direct Specialist Access: In India, patients can directly access specialists without the need for referrals from a general practitioner. This system allows for quicker access to specialized care but can lead to overcrowding of specialist clinics.
- Quality Variation: The quality of healthcare in India varies significantly based on income and location. Urban areas, especially in major cities, typically have high-quality private hospitals, while rural areas may have limited access to advanced medical facilities.
- Appointment Flexibility: Many clinics and hospitals in India offer walk-in services, reducing waiting times for appointments. However, this can also lead to long queues and unpredictable waiting times at popular healthcare facilities.
- Emergency Services: Emergencies in India are typically handled by calling local emergency services or going directly to a hospital emergency department. The emergency response system is less standardized compared to Germany
- Healthcare Cards: Unlike Germany, India does not have a universal health insurance card system. Patients often need to carry individual insurance documents or pay out-of-pocket for services.
- Extended Clinic Hours: Many private clinics and hospitals in India offer extended working hours and are open on weekends, providing greater flexibility for patients.
Key Comparisons
- Accessibility: India offers more direct access to specialists, while Germany’s referral system aims to manage resources more efficiently.
- Wait Times: Germany may have longer wait times for specialist appointments, while India’s system can lead to unpredictable waiting times at clinics.
- Quality Consistency: Germany provides more consistent quality across regions, whereas India shows significant variations between urban and rural areas.
- Emergency Response: Germany’s standardized emergency system contrasts with India’s more varied approach to emergency care.
- Appointment Flexibility: Indian clinics often offer more flexible hours and walk-in services, while German clinics typically adhere to more structured schedules.
Hence, while Germany’s system is more structured and offers consistent quality, India’s system provides more direct access and flexibility. However, the quality and accessibility in India can vary greatly depending on location and economic factors.
Medical Appointments
Every healthcare system has its quirks and hiccups, and Germany and India are no exceptions. Let’s dive into some of the challenges you might face in each country – from language barriers to waiting times, and everything in between. Understanding these hurdles can help you navigate your healthcare journey more smoothly, whether you’re in Berlin or Bangalore.
Germany: Language Barriers and Systemic Pressures

- Language Barriers: For expats in Germany, language can be a significant challenge in accessing healthcare. While many doctors in urban areas speak English, finding English-speaking healthcare providers can be difficult, especially in smaller towns or rural areas. Patients often need to prepare questions in German or bring a translator, which can complicate medical consultations and potentially affect the quality of care received.
- Appointment Wait Times: As mentioned briefly earlier, Germany faces challenges with long waiting periods for specialist appointments. This is partly due to a shortage of doctors and nurses, especially in rural areas. Patients may wait several weeks or even months for non-emergency specialist consultation. This can be particularly frustrating for those accustomed to more immediate access to healthcare services.
- Aging Population: Germany’s aging population is putting increasing pressure on the healthcare system. As the proportion of elderly citizens grows, there’s a rising demand for healthcare services, particularly in areas like geriatric care, chronic disease management, and long-term care facilities. This demographic shift is straining resources and contributing to longer wait times across the healthcare system.
- Finding Hausarzt in small towns: Small university towns like Thuringia, see a growth in population due to students inflow, which leads to an increased demand for medical services. There are not many doctors available in small towns sometimes and at the time of high demand, because they may have a full roster of patients.
India: Accessibility and Quality Disparities
- Language Accessibility: In India, language is generally less of a barrier in medical settings, especially in urban areas, due to the widespread use of English in the medical profession. However, in rural areas or among less educated populations, language can still pose challenges, particularly with regional dialects.
- Appointment Availability and Quality Variation: While it’s often easier to get quick appointments in India, especially in private healthcare facilities, the quality of care can vary widely. This disparity in quality is one of the most significant challenges in the Indian healthcare system. Patients may have to navigate between numerous options to find reliable, high-quality care.
- Rural Healthcare Challenges: India faces severe challenges in providing healthcare in rural areas. There’s a significant disparity in the availability of healthcare facilities and specialists between urban and rural regions. Rural areas typically lack basic healthcare infrastructure, leading to limited access to quality medical care for a large portion of the population.
Key Comparisons
- Access vs. Quality: While India often offers quicker access to medical appointments, Germany generally provides more consistent quality of care across its healthcare system.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Both countries face challenges in rural healthcare, but the disparity is more pronounced in India, where rural areas severely lack healthcare infrastructure.
- Language Issues: Language barriers are a more significant issue for expats in Germany, while India’s medical system is generally more accommodating to English speakers.
- System Pressures: Germany’s challenges stem from an ageing population and systemic inefficiencies, while India’s issues are more related to infrastructure gaps and quality inconsistencies.
- Wait Times: Long wait times for specialist appointments are a common complaint in Germany, whereas in India, the challenge is more about finding reliable, high-quality care rather than waiting for appointments.
To summarize, while Germany grapples with systemic pressures and language barriers for expats, India faces more fundamental challenges in ensuring consistent quality and accessibility of healthcare across its vast and diverse population. Both systems have their unique strengths and weaknesses, reflecting the broader socio-economic contexts of their respective countries.
Service Provision in Healthcare
When it comes to actually getting medical care, Germany and India have some interesting differences in how they deliver services. Let’s have a closer look at what you can expect in each country – from your first doctor’s visit to specialist care and hospital stays.
Germany: Comprehensive and Coordinated Care
- Primary Care: As we discussed previously, in Germany, the first point of contact for most medical issues is typically the Hausarzt (General Practitioner). New residents should register with a Hausarzt soon after arrival. This system helps in coordinating overall healthcare and maintaining continuity of care.
- Specialist Care: While the referral system from GPs to specialists is still in place, it has become more flexible. Referrals are often recommended for efficient care coordination and potentially shorter wait times. However, patients can directly access specialists in certain fields like gynaecology, ophthalmology, and paediatrics without a referral.
- Hospital Services: German hospitals provide comprehensive services, mostly covered by health insurance. Public hospitals offer high-quality care, while private hospitals may provide additional amenities like private rooms or more personalized care. The choice between public and private hospitals often depends on the patient’s insurance type and personal preferences.
- Preventive Care: Germany places a strong emphasis on preventive care. Regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations are typically covered by health insurance, encouraging early detection and management of health issues.
India: Direct Specialist Access and Variable Costs

- Direct Specialist Access: In India, patients can often directly consult specialists without referrals from a GP. This system allows for quicker access to specialized care but can lead to overcrowding of specialist clinics and potentially unnecessary consultations.
- Public vs. Private Healthcare: Public hospitals in India offer basic services at lower costs, but often face challenges of overcrowding and limited resources. Private hospitals, particularly in urban areas, provide advanced care and better facilities but at significantly higher costs.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: A significant portion of healthcare costs in India are paid out-of-pocket, especially for specialized treatments and private healthcare services. This can lead to financial strain for many patients, particularly for complex or long-term treatments.
- Urban-Rural Divide: There’s a notable disparity in healthcare provision between urban and rural areas in India. Urban centres typically have advanced medical facilities and a higher concentration of specialists, while rural areas may lack basic healthcare infrastructure.
Key Comparisons
- Care Coordination: Germany’s system emphasizes coordinated care through GPs, while India’s system allows more direct access to specialists but with less coordination.
- Cost Structure: In Germany, most healthcare costs are covered by insurance, minimizing out-of-pocket expenses. In India, out-of-pocket costs can be significant, especially for private healthcare.
- Quality Consistency: Germany offers more consistent quality across its healthcare system, while in India, quality can vary significantly between public and private sectors, and between urban and rural areas.
- Preventive Care: Germany’s system places a strong emphasis on preventive care, which is less pronounced in India’s healthcare approach.
- Specialist Access: While Germany generally requires referrals for specialist care, India offers more direct access to specialists, though often at higher personal costs.
In conclusion, while Germany’s healthcare system focuses on comprehensive, coordinated care with minimal out-of-pocket costs, India’s system offers more direct access to specialists but with greater variability in costs and quality. Both systems have their strengths and challenges, reflecting the broader healthcare priorities and resources of each country.
Practical Tips for Navigating Healthcare in Germany
Now that we have explained how the German healthcare system works and how it compares with its Indian counterpart, here are a few practical tips that can make your healthcare experiences in Germany smooth and well-informed.
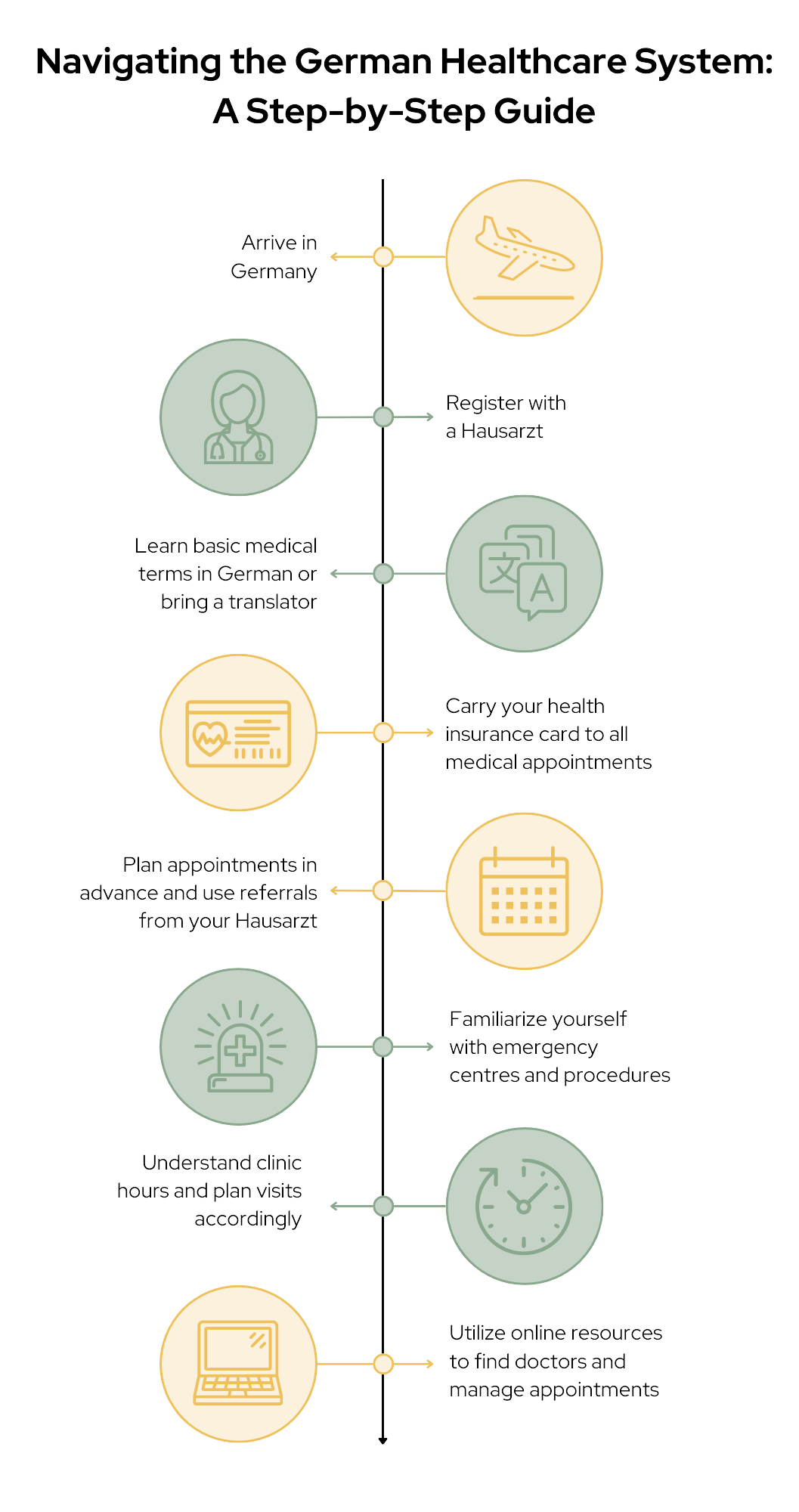
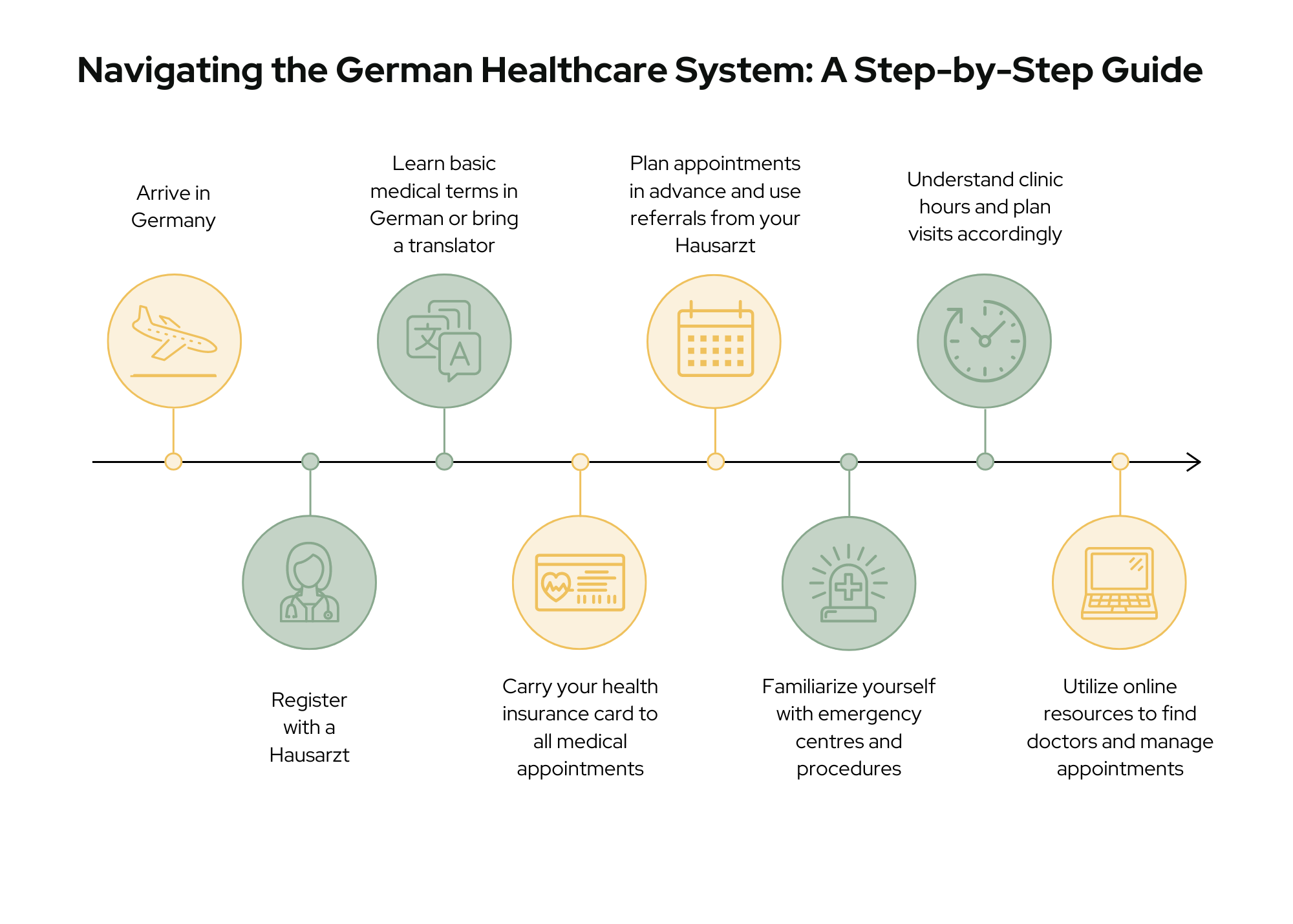
- Register with a Hausarzt
As soon as you arrive in Germany, it’s crucial to find and register with a Hausarzt. The Hausarzt will be your first point of contact for most medical issues and can provide referrals to specialists if needed. Having a dedicated GP helps in maintaining continuity of care and ensures you have a trusted medical advisor.
- Language Preparation
While many doctors in urban areas speak English, it’s helpful to learn basic medical terms in German or bring a translator to appointments. This can ease communication and ensure you understand your treatment options. Preparing questions in German or using translation apps can also be beneficial.
- Health Insurance Card
Always carry your health insurance card (Gesundheitskarte) to all medical appointments. This electronic card is essential for accessing healthcare services and ensures that your treatments are covered by your insurance. It contains important information that healthcare providers need to process your visits and treatments.
- Plan for Appointments
Be prepared for potential waiting times, especially for specialist appointments. Booking appointments well in advance and using referrals from your Hausarzt can help reduce wait times. It’s also a good idea to schedule routine check-ups and non-urgent consultations ahead of time to avoid long waits.
- Emergency Services
In case of emergencies, you can walk into emergency centres (Notaufnahme) or call the emergency number 112. Familiarize yourself with the locations of nearby emergency centres and understand the procedures for accessing emergency care. Knowing where to go and what to do in an emergency can save valuable time.
- Understand Clinic Hours
Note that many clinics in Germany have specific operating hours and may close in the afternoons on certain days, such as Wednesdays and Fridays. Plan your visits accordingly to avoid inconvenience. Some clinics may offer extended hours or weekend services, so check their schedules in advance.
- Utilize Online Resources
Use online platforms and patient management organizations to navigate the healthcare system, find doctors, and manage appointments. Websites like Apotheken Umschau can provide valuable information on medications and healthcare services. Many healthcare providers also offer online appointment booking and consultation services.
Tip: Leveraging Barmer Health Insurance through Feather for Optimal Care
For Indian expats in Germany, securing reliable health insurance is crucial. Barmer Health Insurance* offers comprehensive coverage with minimal out-of-pocket costs and English-language services, making it ideal for non-German speakers. Choosing Barmer through Feather adds even more benefits: Feather simplifies the enrolment process, handles documentation, and provides personalized, English-friendly support. This partnership ensures you get the best coverage with minimal hassle, making it an excellent choice for expats.
Conclusion
Navigating the healthcare systems in Germany and India presents unique challenges and opportunities for Indian expats. Germany’s structured and comprehensive approach to healthcare, characterized by universal coverage and coordinated care, offers a reliable safety net, albeit with some hurdles such as language barriers and appointment wait times. On the other hand, India’s healthcare system provides direct access to specialists and greater flexibility, but it also faces significant disparities in quality and accessibility, particularly between urban and rural areas. By understanding the differences in healthcare structures, challenges, and service provisions, Indian expats can better equip themselves to make informed decisions about their healthcare needs.
* This article contains affiliate links. If you click on the product links in this article and make a purchase, we earn a small commission. It won’t make any difference to you in price. We only recommend products and services we trust and believe will be beneficial to our readers. This helps support our efforts in bringing you valuable content. Thank you for your support!
